
Home News Industry-news Early stationary phases of gas-solid chr…
Porous polymer beads were obtained by Hollis in 1966 through copolymerization of styrene and divinylbenzene, he conducted a detailed study on the chromatographic separation performance of such polymers, calling them Porpak. The Porpak Q he is studying is a gas solid chromatography stationary phase with excellent chromatographic separation performance. Soon various brands of Porous polymer beads stationary phases emerged. They are called GDX (Gaofenzi Duokong Xiaoqiu), which is the prefix of the Chinese Pinyin for Porous polymer beads. In the late 1960s, the Institute of Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences also developed this type of polymer porous microsphere stationary phase and named them GDX (Gaofenzi Duokang Xiaoqiu). Afterwards, Tianjin Chemical Reagent Factory II produced
GDX 101、GDX 102、GDX 103、GDX 104、GDX 105、GDX 201、GDX 301、GDX 501 and other brands,Shanghai Chemical Reagent Factory has produced Porous polymer beads called "401.... 404 organic carriers".
(1)Characteristics of GDX
a、GDX has strong hydrophobicity, and the water peak can be washed out after ethane, providing an excellent chromatographic stationary phase for the determination of trace amounts of water in organic compounds.
b、GDX is spherical and uniformly sized, which facilitates the filling of chromatographic columns and improves column efficiency.
c、By changing the polymerization process conditions, the polarity and pore size of GDX can be altered to produce polymer porous microspheres with various properties.
(2) Preparation of GDX
GDX is obtained by suspension polymerization of divinylbenzene and styrene in water。It is to disperse the monomer to be polymerized in water and copolymerize under the action of an initiator. Due to the addition of a certain amount of solvent as a diluent in the raw material, the diluent does not react during the polymerization process, but it will occupy a certain space in the small ball, and after polymerization, the diluent will be expelled, forming many small pores in the polymer porous small ball. The structure of GDX is shown in the picture below:
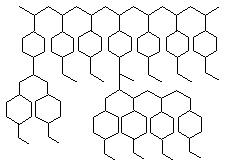
(3) Properties of GDX
GDX is a white or slightly yellow sphere, the specific surface area ranges from tens to hundreds of m2/g, with an apparent density of 0.1-0.5 g/mL, and can generally withstand high temperatures of 250-270℃.
(4) Application of GDX
Determination of trace amounts of water in organic matter: For example, in the synthesis of butadiene rubber, it is required that the water content of the monomer butadiene be below 3 × 10-5 g/mL, and a 100 cm × 0.4cm i.d. GDX-105 chromatographic column is used. Trace amounts of water in organic solvents and hydrogen chloride can be determined using GDX-104 columns.
Determination of semi water gas composition: Separating CH4, CO, CO2 on GDX-104 column through valve switching by using a series column of GDX-104 (3.7m) and molecular sieve (3.0m). Separating O2 and N2 on a molecular sieve column can prevent CO2 from passing through the molecular sieve column.
Since Hollis developed polymer porous microspheres, there have been many further studies, but there have been no further breakthroughs, only a lot of research work in expanding applications.
Name: Jimy Ji
Mobile:+86 18915768767
Tel:+86 13646226232
Whatsapp:8615370757815
Email:sale@tsingcarbo.com
Add:No.5, Wujing Road, Economic and Technological Development Zone, Kunshan, Suzhou, China